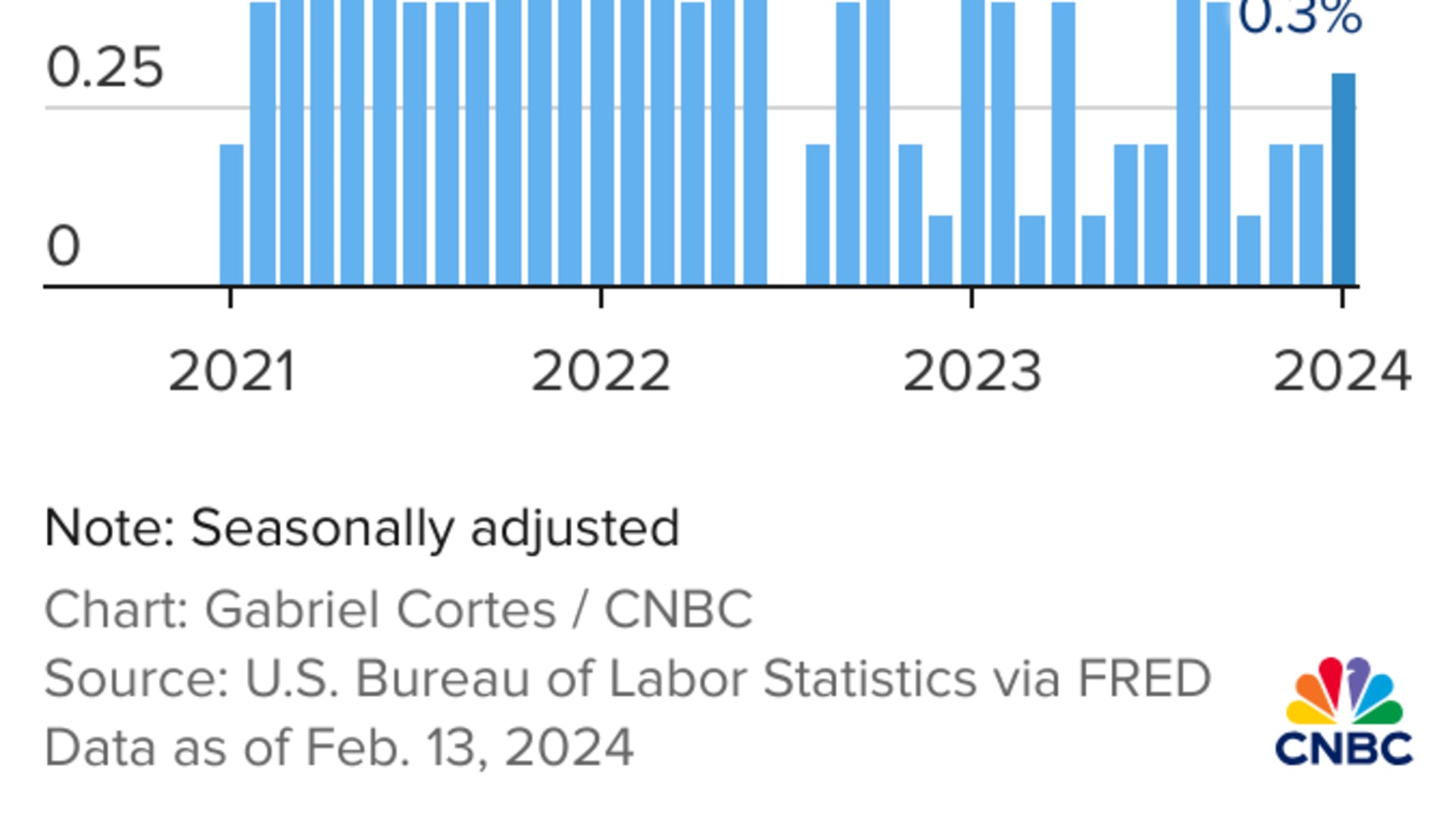
- The consumer price index increased 0.3% in January, the Bureau of Labor Statistics reported. On a 12-month basis, that came out to 3.1%, down from 3.4% in December.
- Shelter prices accounted for much of the rise, climbing 0.6% on the month, contributing more than two-thirds of the headline increase. On a 12-month basis, shelter rose 6%.
- Stocks slid sharply following the release and Treasury yields surged higher.
Inflation rose more than expected in January as stubbornly high shelter prices weighed on consumers, the Labor Department reported Tuesday.
The consumer price index, a broad-based measure of the prices shoppers face for goods and services across the economy, increased 0.3% for the month, the Bureau of Labor Statistics reported. On a 12-month basis, that came out to 3.1%, down from 3.4% in December.
Economists surveyed by Dow Jones had been looking for a monthly increase of 0.2% and an annual gain of 2.9%.
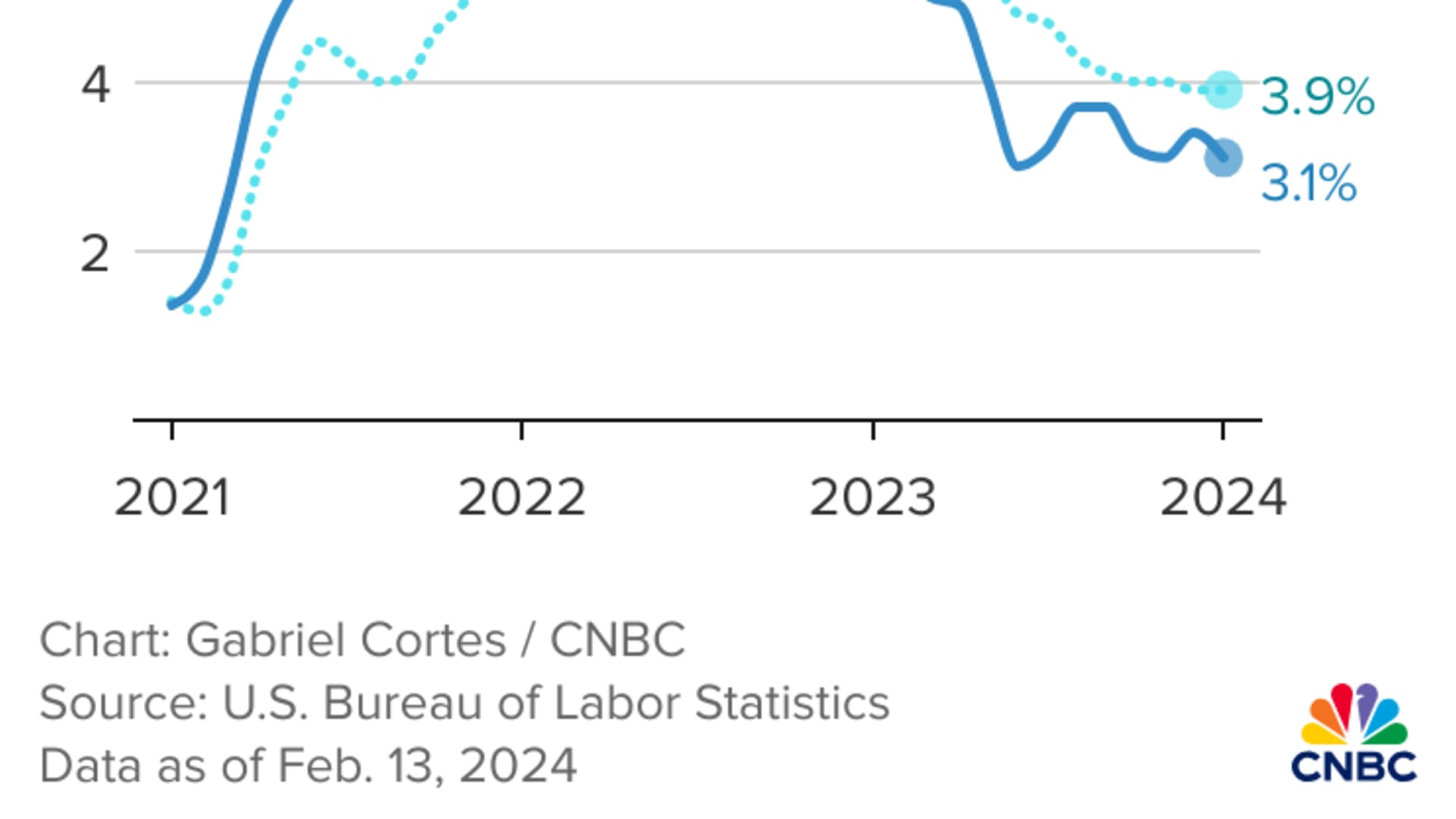
Excluding volatile food and energy prices, the so-called core CPI accelerated 0.4% in January and was up 3.9% from a year ago, unchanged from December. The forecast had been for 0.3% and 3.7%, respectively.

Shelter prices, which comprise about one-third of the CPI weighting, accounted for much of the rise. The index for that category climbed 0.6% on the month, contributing more than two-thirds of the headline increase, the BLS said. On a 12-month basis, shelter rose 6%.
Money Report
Food prices moved higher as well, up 0.4% on the month. Energy helped offset some of the increase, down 0.9% due largely to a 3.3% slide in gasoline prices.
Stock market futures fell sharply following the release. Futures tied to the Dow Jones Industrial Average were off more than 250 points and Treasury yields surged higher.
Even with the rise in prices, inflation-adjusted hourly earnings increased 0.3% for the month. However, adjusted for the decline in the average workweek, real weekly earnings fell 0.3%. Real average hourly earnings rose 1.4% from a year ago.
"Inflation is generally moving in the right direction," said Lisa Sturtevant, chief economist at Bright MLS. "But it's important to remember that a lower inflation rate does not mean that prices of most things are falling — rather, it simply means that prices are rising more slowly. Consumers are still feeling the pinch of higher prices for the things they buy most often."
The release comes as Federal Reserve officials look to set the proper balance for monetary policy in 2024. Though financial markets have been looking for aggressive interest rate cuts, policymakers have been more cautious in their public statements, focusing on the need to let the data be their guide rather than preset expectations.
Fed officials expect inflation to recede back to their 2% annual target in large part because they think shelter prices will decelerate through the year. January's increase could be problematic for a central bank looking to take its foot off the brake for monetary policy at its tightest in more than two decades.
"The much-anticipated CPI report is a disappointment for those who expected inflation to edge lower allowing the Fed to begin easing rates sooner rather than later," said Quincy Krosby, chief global strategist at LPL Financial. "Across the board numbers were hotter than expected making certain that the Fed will need more data before initiating a rate cutting cycle."
Generally, the inflation data had been encouraging, even if annual rates remain well above the Fed's 2% target. Moreover, core inflation, which officials believe is a better guide of long-run trends, has been even more stubborn as housing costs have held higher than anticipated.
In recent days, policymakers including Chair Jerome Powell have said the broader strength of the U.S. economy gives the Fed more time to process data as it doesn't have to worry about high rates crushing growth.
Market pricing before the CPI release indicated a tilt toward the first rate cut coming in May, with a likely total of five quarter-percentage point moves lower before the end of 2024, according to CME Group data. However, several Fed officials have said they think two or three cuts are more likely.
Outside of the jump in shelter costs, the rest of the inflation picture was a mixed bag.
Used vehicle prices declined 3.4%, apparel costs fell 0.7% and medical commodities declined 0.6%. Electricity costs rose 1.2% and airline fares increased 1.4%. At the grocery store, ham prices fell 3.1% and eggs jumped 3.4%.
Don't miss these stories from CNBC PRO:
- Three stocks that could replace Tesla in the 'Magnificent 7'
- Morgan Stanley hikes Nvidia price target ahead of earnings: 'AI demand continues to surge'
- Vanguard launches two new ETFs to hit this sweet spot of tax-free fixed income
- Berkshire Hathaway topped $600,000 a share last week, aiming at $1 trillion market value






